how to draw molecular orbital diagram for heteronuclear molecules
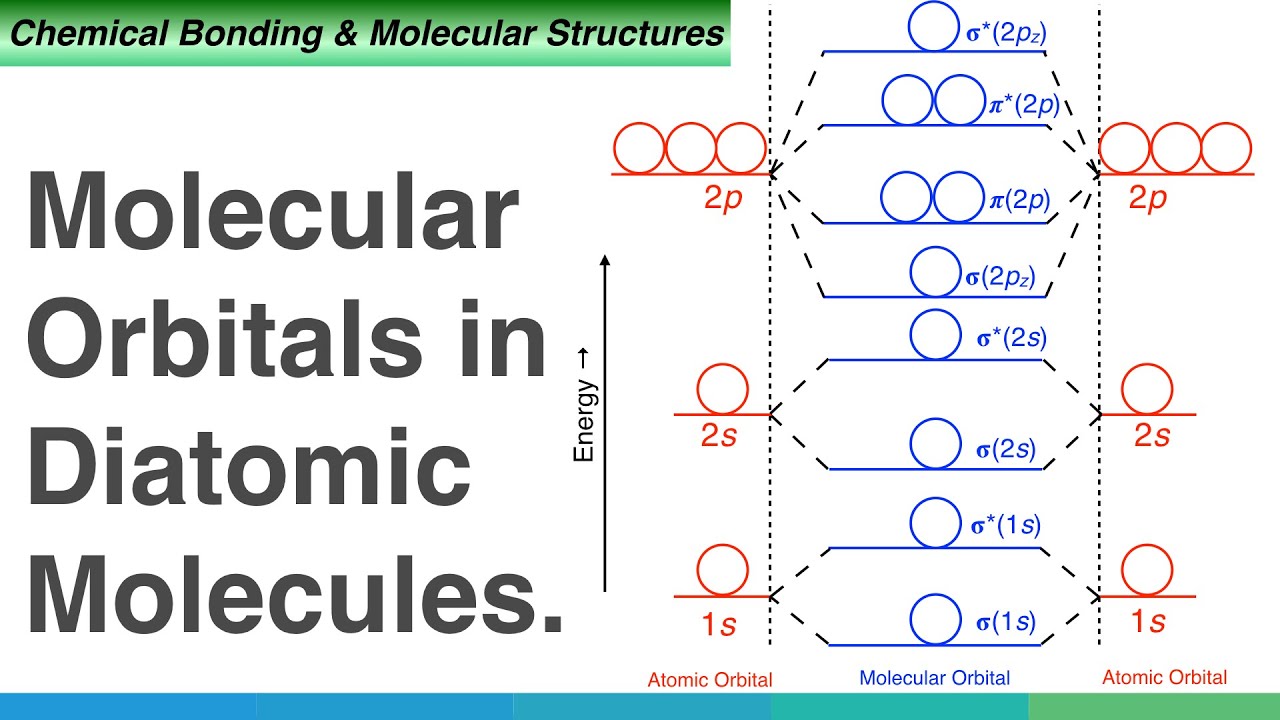
Molecular Orbital Diagrams. LCAO MOs with p-orbitals The following is a general LCAO MO diagram for the formation of X2 where 2s and 2p.

Molecular Orbital Diagrams Simplified By Megan A Lim Medium
Based on the amount of orbital overlap the relative changes in energy differ going from the atomic orbital to the molecular orbital.

. In case of beryllium hydride there are 3 atoms overlapping simultaneously. We will consider the molecular orbitals in molecules composed of two identical atoms H2 or Cl2 for example. Contour maps of the molecular orbital charge densities of the LiH CH HF diatomic hydrides.
1 sigma bonding 2 sigma antibonding 3 pi bonding and 4 pi antibonding. The bonds between atoms in molecules have different shapes sizes and strengths depending on which atoms are bonded together. Learn how to apply molecular orbital theory to determine the shapes.
Involving heavier atoms makes it harder to guess at molecular orbital diagrams and there is need for quantum chemistry calculations. Now MO diagrams are only simple for elements of the second row of the periodic table ceLi through ceNe. The further to the right your element is the lower its energy levels are.
The best way to learn how to draw MO diagrams is to work on practice problems. Density diagrams of the molecular orbitals for the LiH CH and HF molecules are illustrated in Fig. In molecular orbital theory sigma and pi mean the same thing that they meant in valence bond theory with a few exceptions.
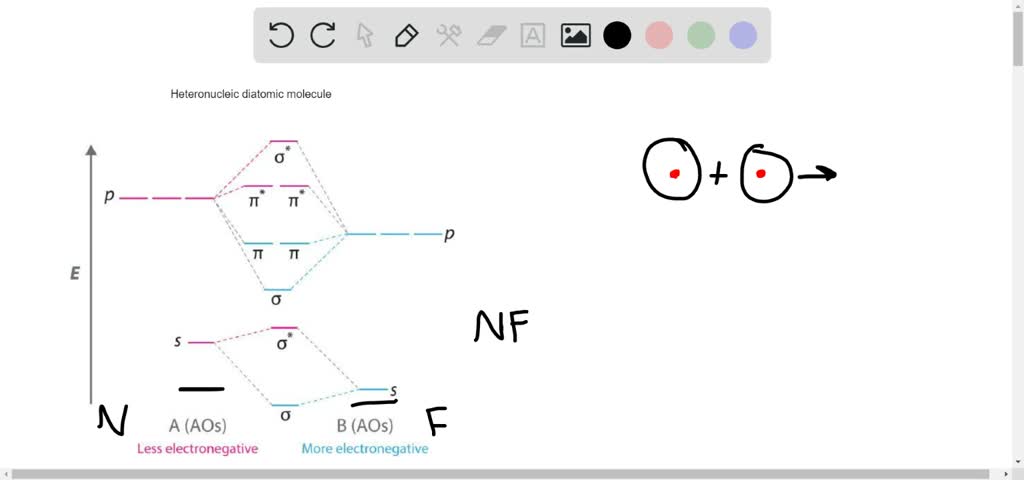
-identify the atom with the greatest Zeff as the atomic orbitals of this atom will lie lower in energy. View Lecture 9 - Molecular Orbital Theory IIpdf from CHEM 3030 at York University. HF nb σ σ Energy H 136 eV 1s F 186 eV 402 eV 2s 2p So HF has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine.
Heteronuclear diatomic molecules 302. Fill the molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy being sure to obey the Pauli principle and Hunds rule. We label a molecular orbital sigma 2s only when it correlates to two atomic 2s orbitals.
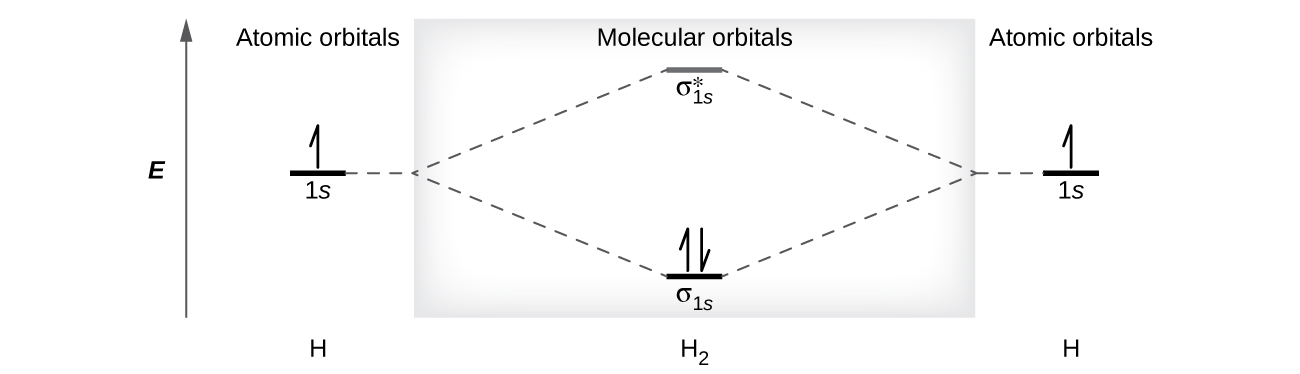
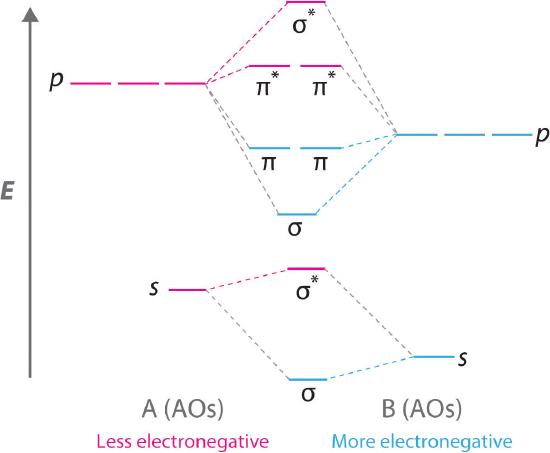
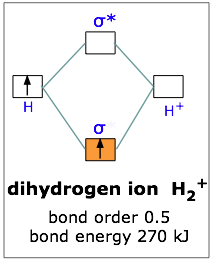
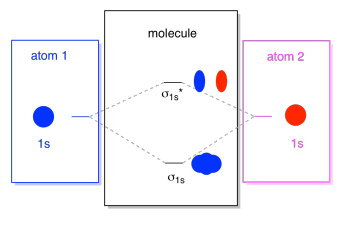
This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2. However recall that the more electronegative atom will be lower on the diagram. Looking at Ne2 molecular orbitals we see that the order is consistent with the generic diagram shown in the previous section.
Atomic valence electrons shown in boxes on the left and right fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones just as is the case for atomic. Draw the two molecular orbitals that are formed from each pair of atomic orbitals in a second period. Using Orbital Hybridization and Valence Bond Theory to Predict Molecular Shape Quiz Molecular Orbital Theory.
The nodes are indicated. -Identify pairs of atomic orbitals that can overlap-they should be close in energy and must be of appropriate. In polyatomic molecules we can have more than two atoms combining eg.
The F 2s is nonbonding. -List the occupied atomic orbitals of both atoms labelling core and valence orbitals. The way these bonds are.
Building Molecular Orbital Diagrams for Homonuclear and Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules. Greater overlap greater change in. Draw the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for this system and determine the total number of valence electrons in S 2.
The 2s orbital on Li is large and diffuse and will overlap extensively with the 1s orbital on H. Postulates of Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter i Matter is composed of small tiny particles called molecules. The g and u subscripts no longer apply because the molecule lacks a center of symmetry.
Thus the rule becomes. MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. In heteronuclear diatomic molecules atomic orbitals only mix when the electronegativity values are similar.
The orbital box diagrams are listed for the first 20 elements in the figure below. Describe how to draw a molecular orbital diagram for a heteronuclear diatomic molecule. With molecular orbitals that correlate to more than one type of atomic orbital we have to use an alternative notation where each set of molecular orbitals of a certain type sigma pi is numbered from lowest energy to highest energy as seen in the textbook.
There are now four types of orbitals to concern ourselves with. In carbon monoxide CO the oxygen 2s orbital is much lower in energy than the carbon 2s orbital so the degree of mixing is low. Firstly we now add our newly acquired antibonding molecular orbitals.
Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules 19. Constructing MO diagrams for heteronuclear molecules require the same 4 steps as above. AO2pz AO2pz σ2pz σ 2pz strong head-on overlap Thus we take 10 atomic orbitals and generate 10 molecular orbitals in accordance with the conservation of orbitals.
Molecular Orbitals In Diatomic Molecules Youtube
Solved When Applying Mo Theory To Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules The Atomic Orbitals Used May Be Of Different Energies If Two Atomic Orbitals Of Different Energies Make Two Molecular Orbitals How Are The Energies

Heteroatomic Molecular Orbital Diagrams Youtube
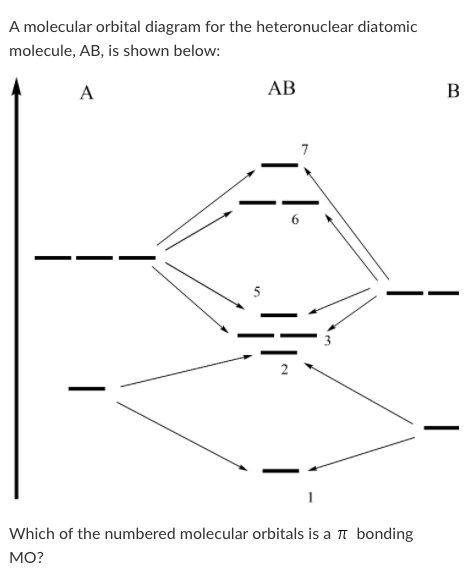
Solved A Molecular Orbital Diagram For The Heteronuclear Chegg Com

Molecular Orbital Theory For Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Pt 4 Youtube
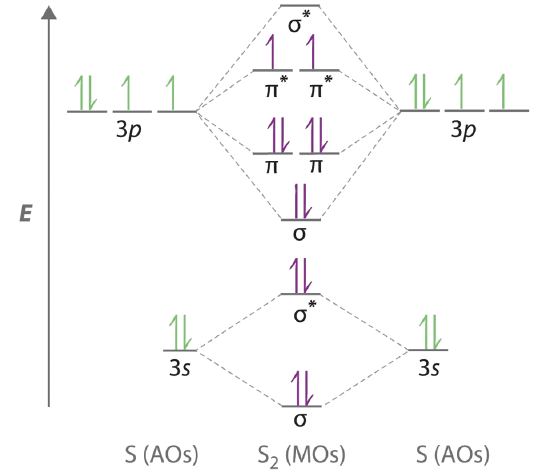
9 8 Second Row Diatomic Molecules Chemistry Libretexts

Molecular Orbital Theory For Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Pt 3 Youtube
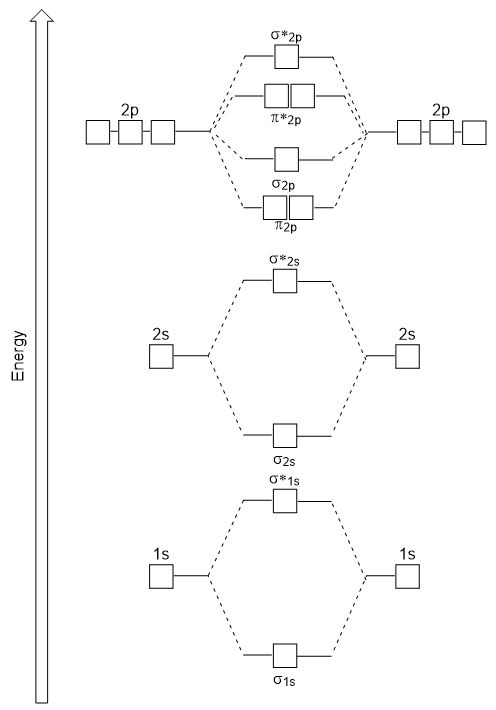
Molecular Orbitals Introductory Chemistry 1st Canadian Edition
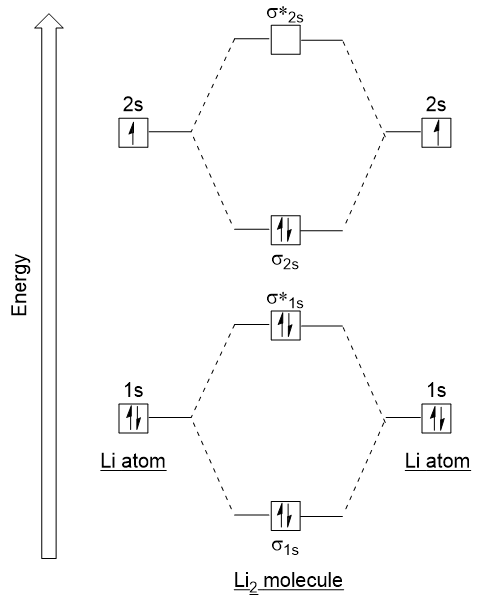
Molecular Orbitals Introductory Chemistry 1st Canadian Edition
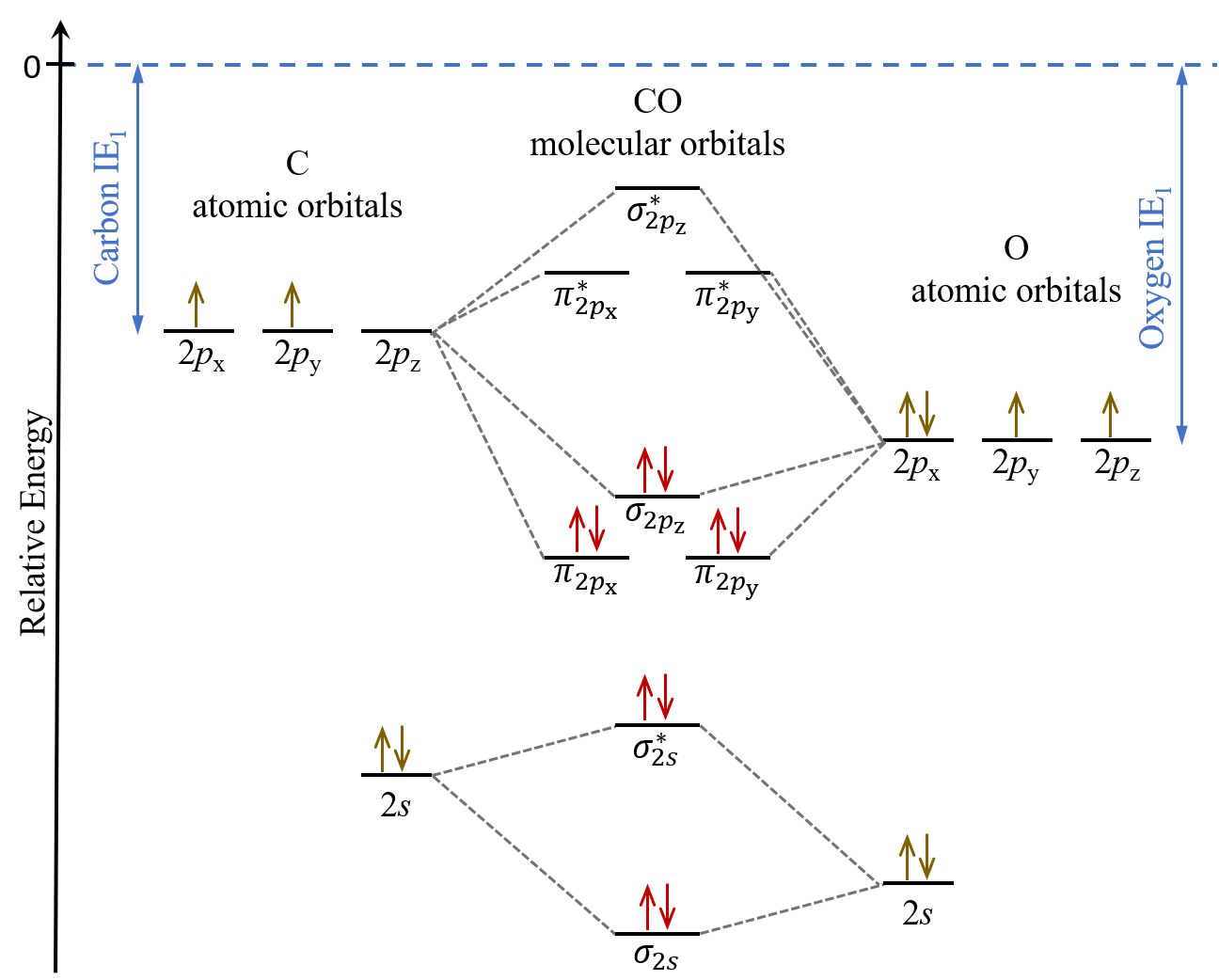
D6 5 Mos For Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Chemistry 109 Fall 2021

Cohesion And Surface Tension Ciencia
1 1 4 5 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Libretexts
Molecular Orbitals Molecular Orbitals For Heteronuclear Molecules
2 5 5 Molecular Orbital Diagrams Chemistry Libretexts
Mo Diagrams For First Row Diatomic Molecules Chemistry Libretexts
3 3 4 Assembling A Complete Mo Diagram Chemistry Libretexts